West Prussia (Westpreußen), Prussia, German Empire Genealogy
Guide to West Prussia (Westpreussen), German Empire ancestry, family history, and genealogy before 1945: birth records, marriage records, death records, both church and civil registration, compiled family history, and finding aids.
| West Prussia (Westpreussen), German Empire Wiki Topics | |||||||

| |||||||
| Getting Started | |||||||
| Major West Prussia (Westpreussen) Record Types | |||||||
| Reading the Records | |||||||
| Additional West Prussia (Westpreussen) Record Types | |||||||
| West Prussia Background | |||||||
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| Local Research Resources | |||||||
| Germany Record Types | |||||||
| Germany Background | |||||||
| |||||||
In this region, part of Germany which was lost to other countries after World War II, many records, both church/parish registers and civil registration records, were damaged, destroyed, or misplaced.
Historical Background[edit | edit source]
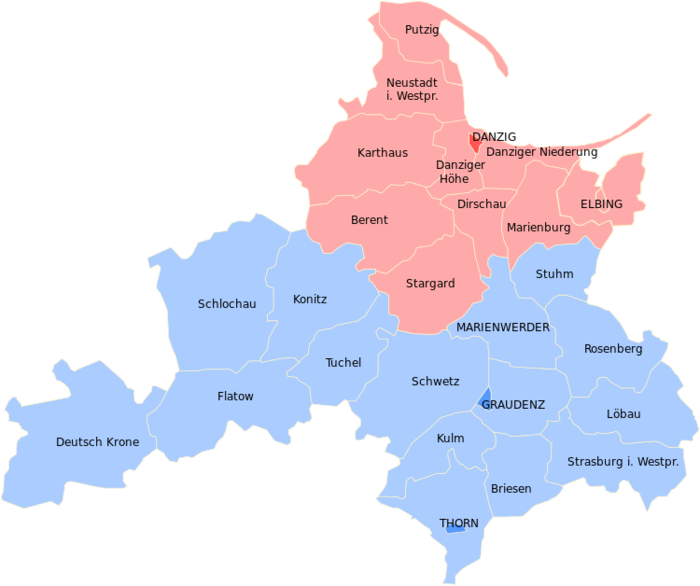
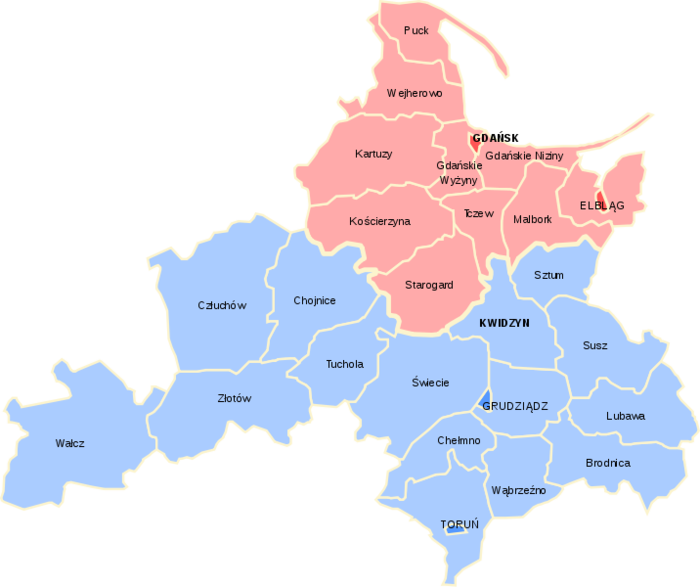
- The Province of West Prussia (German: Provinz Westpreußen) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1922.
- West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
- West Prussia was dissolved in 1829 and merged with East Prussia to form the Province of Prussia, but was re-established in 1878 when the merger was reversed and became part of the German Empire.
- From 1918, West Prussia was a province of the Free State of Prussia within Weimar Germany, already losing most of its territory to the Second Polish Republic.
- West Prussia was dissolved in 1922, and its remaining western territory was merged with Posen to form Posen-West Prussia, and its eastern territory merged with East Prussia as the Region of West Prussia district.
- West Prussia was notable for its ethnic and religious diversity due to immigration and cultural changes, with the population becoming mixed over the centuries. Since the early Middle Ages the region was inhabited by numerous Slavic and Baltic peoples, such as Pomeranians in the Pomerelia region, Old Prussians and Masovians in Kulmerland, and Pomesanians east of the Vistula River. Later, Germans followed. Germans were also the largest group in West Prussia until its dissolution in 1922, with large numbers of Kashubians, Poles, Mennonites, and Jews also settling in the region.
- Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia (German: Reichsgau Danzig-Westpreussen) was a Nazi German province created on 8 October 1939 from annexed territory of the Free City of Danzig, the Greater Pomeranian Voivodship (Polish Corridor), and the Regierungsbezirk West Prussia. Before 2 November 1939, the Reichsgau was called Reichsgau West Prussia. Though the name resembled that of the pre-1920 Prussian province of West Prussia, the territory was not identical. Unlike the former Prussian province, the Reichsgau included the Bromberg (Bydgoszcz) region in the south and lacked the Deutsch-Krone (Wałcz) region in the west.
- During World War II, the region was settled with 130,000 German colonists, while between 120,000 and 170,000 Poles and Jews were removed by the Germans.
- Later in the war, many West Prussian Germans fled westward as the Red Army advanced on the Eastern Front.
- All of the areas occupied by Germany were restored to Poland in 1945.
- The vast majority of the remaining German population of the region which had not fled before was subsequently expelled westward.[1]
Getting Started[edit | edit source]
Getting Started with Germany ResearchLinks to articles on getting started with German research: |
Germany Research ToolsLinks to tools and websites that assist in German research: |
Historical Geography[edit | edit source]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1919: Became Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland (Map) |
Finding Birth, Marriage, and Death Records for West Prussia (Westpreussen)[edit | edit source]
Most of the information you need to identify you ancestors and their families will be found in two major record groups: civil registration and church records. To locate these records, follow the instructions in these Wiki articles.
1. Find the name of your ancestor's town in family history records.[edit | edit source]
Records were kept on the local level. You must know the town where your ancestor lived. If your ancestor was a United States Immigrant, use the information in the Wiki article Germany Finding Town of Origin to find evidence of the name of the town where your ancestors lived in Germany.
Also, see:
- Ausländerakten, 1812-1895 Record of Polish and Russian workers and immigrants in the district of Marienwerder, Westpreußen, Germany. Includes those expelled.
- Germany Displaced Persons Research: If your ancestors were evacuated from their homes at the end of World War II, see this article.
2. Use gazetteers and/or parish register inventories to learn more important details.[edit | edit source]
Your ancestor's town might have been too small to have its own parish church or civil registration office. Find the location of the Catholic or Lutheran (Evangelical) parish that served your ancestor's locality. Find the name of the civil registration office (Standesamt) that serves your ancestor's locality. Use the Wiki article Finding Aids For German Records for step-by-step instructions.
Germany was first unified as a nation in 1871. An important gazetteer, Meyers Orts- und Verkehrs-lexikon des deutschen Reichs, "Meyer's Gazetter" for short, details the place names of villages, towns, counties (kreise), and higher jurisdictions used at that time. In the Research Wiki, FamilySearch Catalog, and FamilySearch Historical Records, the records of Germany are organized using those place names.
At the end of both World Wars, the boundaries of the states were changed dramatically, as areas of Germany were distributed among the Allied nations. Eventually, after re-unification in 1990, the states of Germany settled into what they are today. It is also necessary to understand Germany by this system, as it affects the locations of civil registration offices, archives, and mailing addresses used in correspondence searches.
Use Westpreussen.de for detailed information.[edit | edit source]
1. Enter the town name in the search field.
2. A list of towns by that name, with basic info will come up. For your town, click on "Details" in the far right column.
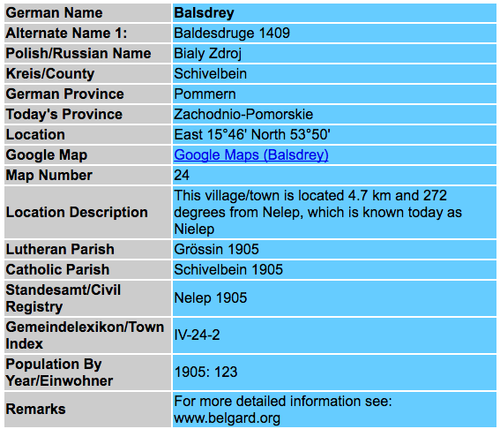
Example entry: This information will be on the details page. Notice that the listed names of the registry office, Protestant church, and Catholic church are links. Clicking on those links will give even further details.
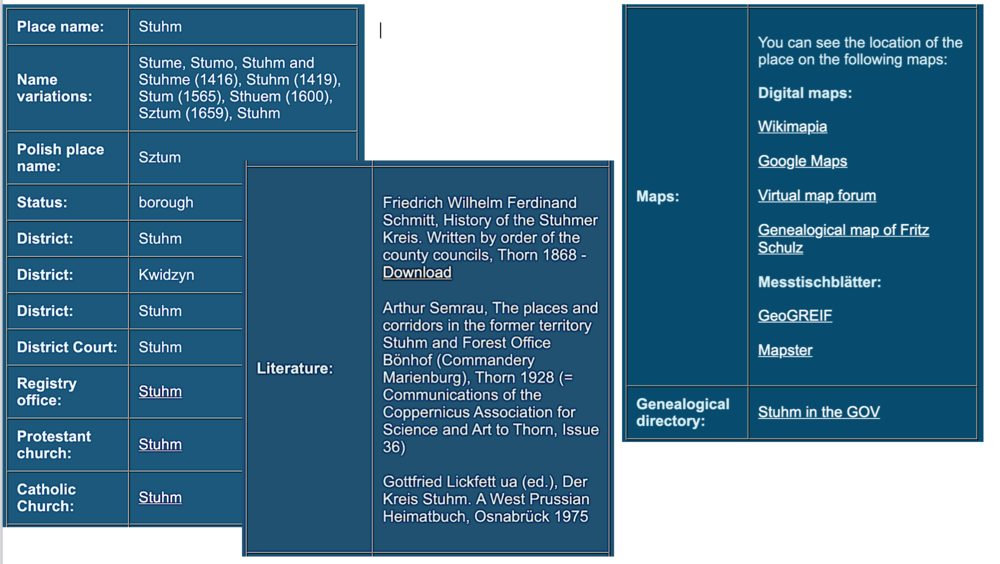
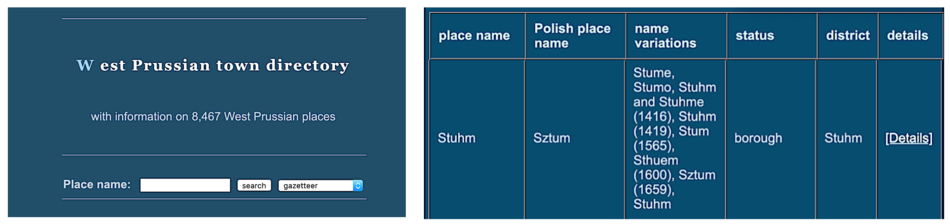
Consult Kartenmeister for parish and Standesamt information.[edit | edit source]
If Kartenmeister is having temporary technical difficulties, check back later.
For the provinces of East Prussia (Ostpreussen), Posen, Pomerania (Pommern), Silesia (Schlesien), parts of Brandenburg, and West Prussia (Westpreussen), areas which no longer belong to Germany, the online gazetteer Kartenmeister most efficiently tells you parish information:
Example:
3. For birth, marriage, and death records after 1 October 1874, use civil registration.[edit | edit source]
Follow the instructions in West Prussia (Westpreussen), German Empire Civil Registration.
4. For baptism, marriage, and death records, use church records or parish registers.[edit | edit source]
Follow the instructions in West Prussia (Westpreussen), German Empire Church Records.
More Research Strategies and Tools[edit | edit source]
- Germany Online Classes and Tutorials
- German Paleography Seminar - Lessons on German Handwriting
- Old German Script Transcriber (alte deutsche Handschriften): See your family names in the script of the era. Type your name or other word into the font generator tool. Click on the 8 different fonts. Save the image to your computer and use it as you work with old Germanic records.
- Finding Aids for German Records
- Research Tips and Strategies
- German Research, BYU Independent Study, no cost.
- These printable handouts can be used for ready reference when reading German Handwriting.
- Letters:
- Vocabulary found on Specific Records:
- Dates, Numbers, Abbreviations:
- Miscellaneous Vocabulary:
- Fraktur:
- Fraktur Font -- Many forms and books are printed in this font.
- German Given Names:
- List of Names in Old German Script -- A comprehensive list of German given names, written in old script, with possible variations.
Take These Online Classes to Prepare[edit | edit source]
- German Research: Strategies and Sources for Eastern Provinces. Be sure to download the class syllabus.
- Watch the Specific Geography portion to learn how to use MeyersGaz.org and Kartenmeister.com to get the details of the German and Polish names of your town and its higher jurisdictions.
- Watch the General Resources portion to learn how to check for parish registers using
- The PRADZIAD DatabaseThe PRADZIAD Database
- Szukaj w Archiwach
- The Lost Shoe Box, with links to:
- Archion, Cooperative of protestant archives ($)
- Archives Portal Europe
- Watch the West Prussia or Westpreussen portion, which begins at 45:35 minutes.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Wikipedia contributors, "West Prussia," Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Prussia (accessed September 16, 2019).
.svg.png/450px-German_Empire_-_Prussia_-_West_Prussia_(1878).svg.png)